The United Nations uses a set of three dimensions to help determine a country’s overall health.
The United States, according to the Central Intelligence Agency, has a lower life expectancy than 41 other countries in the world.
According to Sarah Shore-Beck, a kinesiology professor at Ball State University, this makes sense given the global reputation America has—fast food and little exercise. Americans tend to eat more meat and processed foods than people in other nations. In other cultures such as eastern countries, for example, they have a 90:10 diet—90 percent of the foods they digest are plants and 10 percent is meat. Meat is used sparingly in their diets, Shore-Beck says.
Shore-Beck says the biggest reason the United States ranks so low on the list is because people don’t know how to be healthy. She says to become a healthier nation, people need to be more educated in general. People are often confused about what’s best to put inside their bodies because many studies show different results and suggestions.
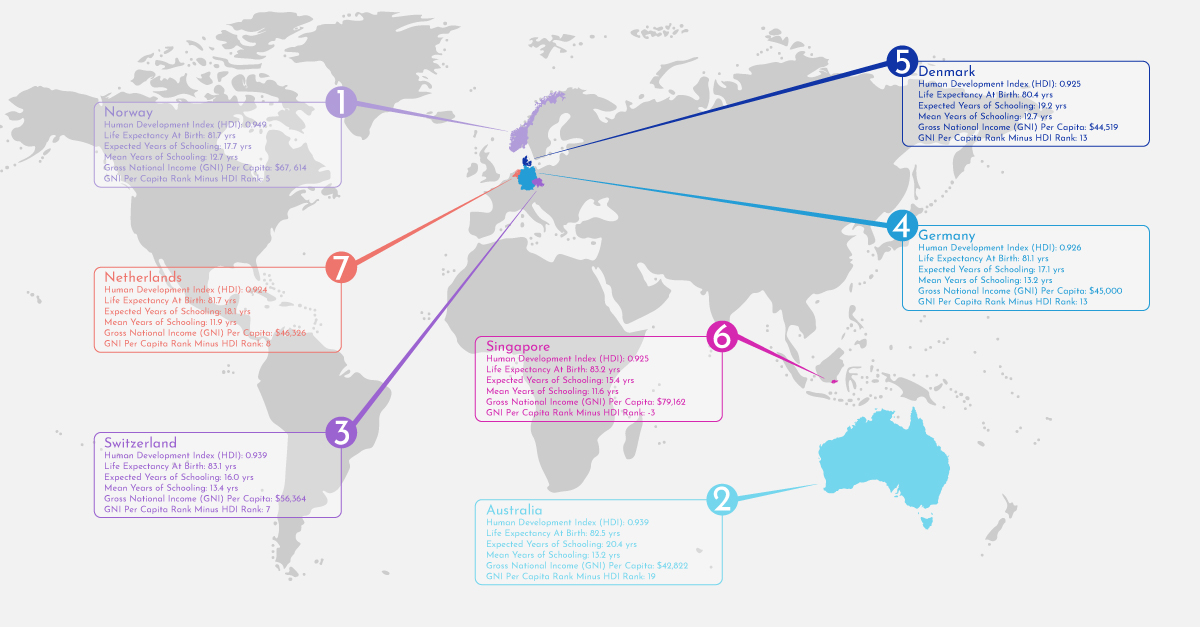
The United Nations Development Programme conducts reports to determine which countries have better human development levels than others. Their 2016 Human Development Report ranked countries by HDI, or Human Development Index. HDI is measured through three dimensions: long and healthy life, knowledge, and a decent standard of living. Long and healthy life is determined by looking at the life expectancy at birth. Knowledge is determined through a country’s expected years of school and the average years of schooling for a country’s population. A decent standard for living is determined by the gross national income per capita. Together, these factors help determine a country’s HDI rank.
Because life expectancy is just one factor for this scale, the United States has an HDI rank of 10, tying with Canada. The seven countries that have the highest ranking can be seen in the graphic below: